Plain Weave
Plain weave is formed by interlacing yarns, with each yarn having one yarn above and one below. Plain weave has good fabric stability.
What is glass fiber filter material? Glass fiber filter material refers to filter materials made from fiberglass, used for purifying fine particles in the air or filtering impurities in liquids such as water and oil. Common glass fiber filter materials include glass fiber primary, medium, and high-efficiency filter paper, glass fiber woven filter fabric, glass fiber non-woven fabric, and glass wool. They are widely used in dust removal systems, HVAC systems, and oil-gas separation fields.
Raw materials for Glass Fiber Filter Material
Fiberglass is made from quartz sand, limestone, dolomite, paraffin, etc., and is spun with soda ash, boric acid, etc. Its main components are silicon dioxide and certain metal oxides. According to composition and performance, glass fiber can be divided into four categories: alkali-free, medium-acid, high-alkali, and special glass fiber; according to form, it can be divided into continuous glass fiber, chopped glass fiber, and glass wool. Glass fiber features flame retardancy, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low moisture absorption, low elongation at break, high tensile strength, brittleness, good thermal insulation and chemical stability, and good electrical insulation.
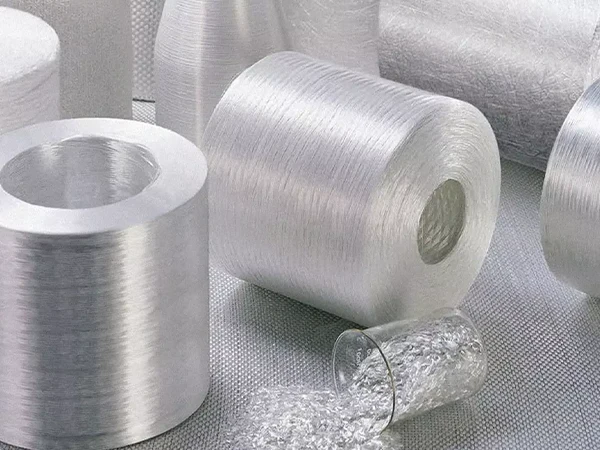

Glass Fiber Production Process
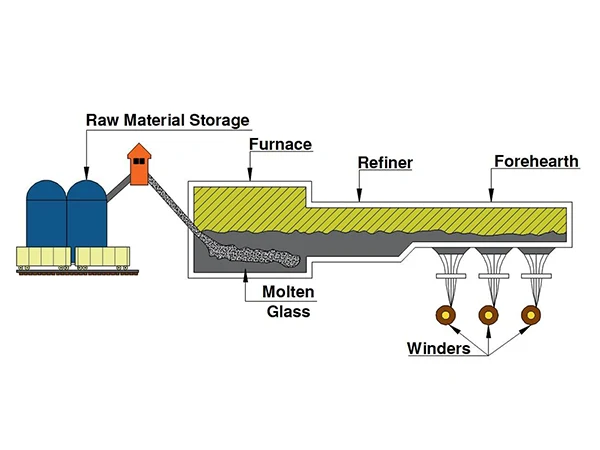
The production processes of glass fiber include the crucible drawing method and the pool kiln drawing method, with the pool kiln drawing being the mainstream process.
Pool kiln drawing method: Talc and limestone are ground into powder and mixed together in a certain ratio. Using natural gas and oxygen as chemical raw materials and electrical energy as the power source, they are burned in a kiln. The combustion temperature is controlled between 1000 °C and 1600 °C. During the combustion process, the mixed powder of talc and limestone melts into a liquid, which flows through a platinum-rhodium precious metal alloy (85:15) porous leak plate and is drawn at high speed into glass primary fibers. These fibers are then condensed with cooling water to form fiberglass. After applying a chemical sizing agent to the surface of the fiberglass, it is dried, packaged, and shipped. The drawing machine is a key piece of equipment in the glass fiber forming process. Its function is to rapidly stretch the glass liquid flowing from the bushing and wind it in a certain direction to form. The performance and precision of the drawing machine directly affect the quality of the fibers.
Features
Types of Glass Fiber Filter Material
Classified by the form of fiberglass, it is divided into glass fiber filter paper, glass fiber woven filter fabric, and glass fiber non-woven filter fabric. Among them, glass fiber filter paper is mainly applied using the wet-laid process, glass fiber woven filter fabric is produced using weaving methods, and glass fiber non-woven filter fabric (glass fiber non-woven filter fabric) is primarily manufactured by needle punching and wet processes. Strictly speaking, glass fiber filter paper belongs to non-woven filter materials. According to the classification of glass fiber filter materials by use, there are glass fiber exhaust filter materials, glass fiber intake filter materials, and glass fiber liquid filter materials.
Glass Fiber Filter Paper
Glass fiber filter paper is a thin sheet made from fine-diameter fiberglass. It has good dimensional stability, high chemical resistance, strong weather resistance, and good non-flammability. It can be made from 100% glass fiber(with a diameter of 0.3–0.5 μm or less, mainly composed of silicon dioxide), lightly beaten, with adhesive added, or mixed with some chemical wood pulp, and formed on a Fourdrinier or cylinder paper machine.
The production of glass fiber filter paper uses a wet-laid process, similar to the production process of regular filter paper. The difference lies in the fact that glass fiber filter paper undergoes mild pulping because glass fiber is brittle. The raw materials used are 100% ultra-fine glass fiber or a certain proportion of wood pulp fibers.
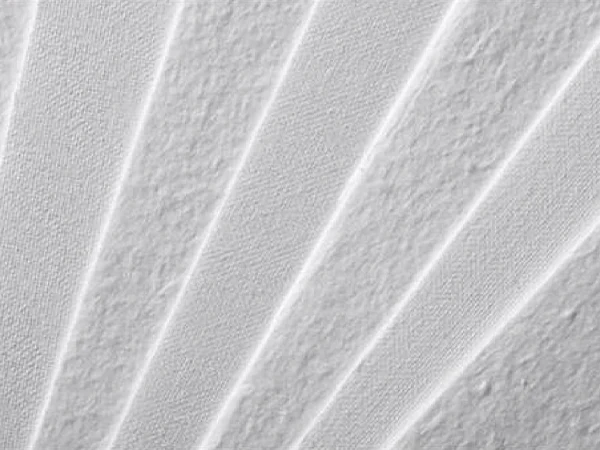

Glass Fiber Woven Filter Fabric
Glass fiber woven filter fabric is a type of filter material made from glass fibe ror glass fiber expanded yarn, offering good high-temperature resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength. Glass fiber woven filter fabric is commonly used in flue gas purification equipment, air filters, and liquid filters to capture solid particles, dust, smoke, and other pollutants, thereby maintaining a clean environment and efficient industrial processes. The raw materials used for glass fiber woven filter fabric include four types: alkali-free glass fiber(long fiber), medium-alkali glass fiber(long fiber), alkali-free glass fiber bulked yarn, and medium-alkali glass fiber bulked yarn.

| Material | Temperature Characteristics | Air Permeability | Single Fiber Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkali-free glass fiber | It can be used long-term at temperatures up to 280 °C, with instantaneous (within 1 hour) temperature resistance up to 350 °C。 | The air permeability of glass fiber expanded yarn filter materials is higher than that of continuous glass fiber filter materials, with glass fiber needle felt materials having the highest air permeability | E-glass fiber can produce fibers with a single fiber diameter of 8–9 μm |
| Medium-alkali glass fiber | The operating temperature of medium-alkali glass fiber filter materials is only 260 °C, with instantaneous temperature resistance below 300 °C。 | -- | |
| Alkali-free glass fiber expanded yarn | It can be used long-term at temperatures up to 280 °C, with instantaneous (within 1 hour) temperature resistance up to 350 °C. | -- | |
| Medium-alkali glass fiber expanded yarn | The operating temperature of medium-alkali glass fiber filter materials is only 260 °C, with instantaneous temperature resistance below 300 °C. | -- |
| Formula Name | Formula Composition | Design Purpose | Applications | Color | Filter Material Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCA (anti-condensation formula) | Mainly composed of water repellent and silicone oil | Designed for dust emission places with high moisture content and low temperature that are prone to condensation | Dust control for cement mills, dryers, etc. | Yellow | Excellent hydrophobicity, good flexural and abrasion resistance |
| FQ | Mainly based on reactive silicone oil | Provide better dust cleaning performance | Mainly used in cement rotary kilns and carbon black industry, etc. | Yellow | Certain hydrophobicity, good flexural and abrasion resistance |
| 165 | Mainly based on graphite | Provide a better cost-performance ratio | Mainly used in the cement industry, etc. | Black | Certain hydrophobicity, flexural and abrasion resistance |
| FS2 (steel formula) | Mainly based on polytetrafluoroethylene and reactive silicone oil | Designed for blast furnace gas purification in the steel industry | Blast furnace gas purification | Yellow | Certain hydrophobicity, good flexural and abrasion resistance |
| PSi | Primarily composed of silicone oil, graphite, and polytetrafluoroethylene | Designed for applications with relatively high flue gas temperatures | For dust emission places with high flue gas temperatures in industries like as building materials | Black | Good temperature resistance, flexibility, flexural and abrasion resistance |
| RH (acid-resistant formula) | Primarily composed of silicone oil, graphite, polytetrafluoroethylene, and acid-resistant components | Provide good acid resistance | Mainly used in cement shaft kilns and the production of 15,000 tons of carbon black | Black | Good hydrophobicity, acid resistance, and flexural and abrasion resistance |
| TFB (high flexural resistance formula) | Primarily composed of polytetrafluoroethylene | Provide excellent flexural and abrasion resistance | For dust removal from high-temperature flue gases in industries such as cement, carbon black, and waste incineration | Yellow | Good flexural and abrasion resistance, hydrophobic properties, and long service life, with some acid resistance |
| AR (high acid resistance formula) | Primarily composed of silicone oil, graphite, polytetrafluoroethylene, and acid-resistant components | Provide excellent acid resistance | Dust removal from acidic atmosphere flue gases in coal-fired boilers and waste incinerators | Black | Excellent hydrophobicity, acid resistance, and good flexural and abrasion resistance. |
| YM (coal-fired boiler formula) | Primarily composed of silicone oil, graphite, polytetrafluoroethylene, and acid-resistant components | Specifically designed for coal-fired boilers | Dust removal from coal-fired boiler flue gas | Black | Excellent hydrophobicity, acid resistance, good flexural and abrasion resistance. |
| B1 | Mainly composed of silicone oil and polytetrafluoroethylene | Designed for the carbon black industry | Pulse dust removal in the carbon black industry | Yellow | Featuring a three-micropore structure, low filtration resistance, and a dust removal efficiency of up to 99.9%. The filtration speed is about twice that of ordinary fabric filter materials. |
| St | Designed for the steel industry | Blast furnace gas purification | Yellow | ||
| Che | Designed for the chemical industry | Gas-solid separation in the chemical industry | Yellow | ||
| JF (interwoven filter material formula) | Mainly composed of water repellent and silicone oil | Specifically designed for glass fiber interwoven filter materials | Dust control for cement mills, dryers, etc. | Yellow | In addition to FCA's anti-condensation properties, it has better flexural resistance |
| F2 (waterproof and oil-proof formula) | Primarily composed of waterproof and oil-proof components | Designed to provide waterproof and oil-proof performance for polyester filter materials | Metallurgy, building materials, etc. | White | Excellent waterproof and oil-proof performance |
Weaving Process of Glass Fiber Woven Filter Fabric

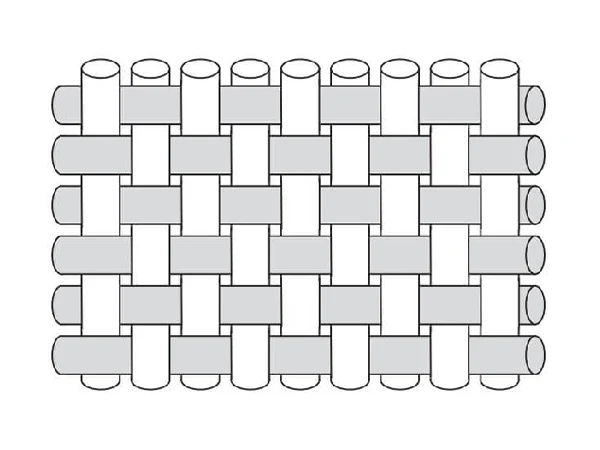
Plain Weave
Plain weave is formed by interlacing yarns, with each yarn having one yarn above and one below. Plain weave has good fabric stability.
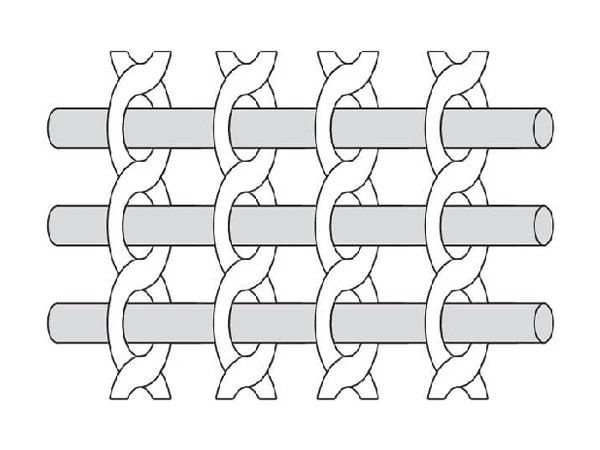
Twill Weave
Twill weave involves two or more filling yarns interlacing alternately. It is characterized by flexibility, smoothness, and strength, but has relatively poor stability.
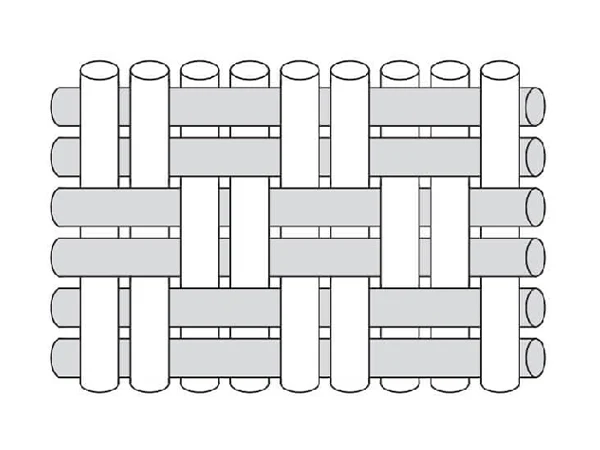
Ribbed Weave
Ribbed weave locks the yarns by intercrossing two or more warp threads with one or more weft threads.
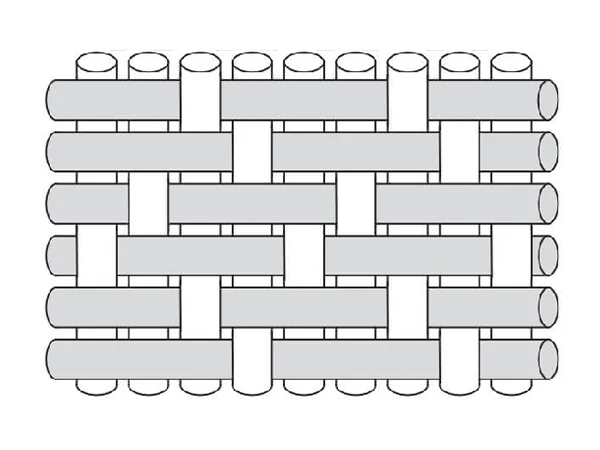
4-Shaft Satin Weave
The 4-shaft satin weave more easily adapts to the typical curved surfaces in reinforced plastics.
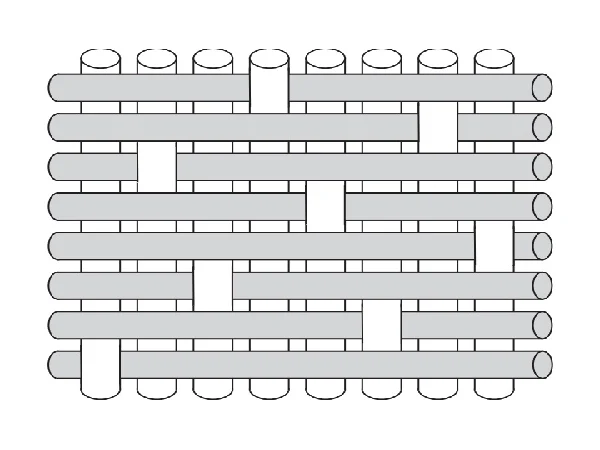
8-Shaft Satin Weave
The 8-shaft satin weave involves one weft thread floating over seven warp threads and under one warp thread. This weave is very flexible and is used to form curved surfaces.
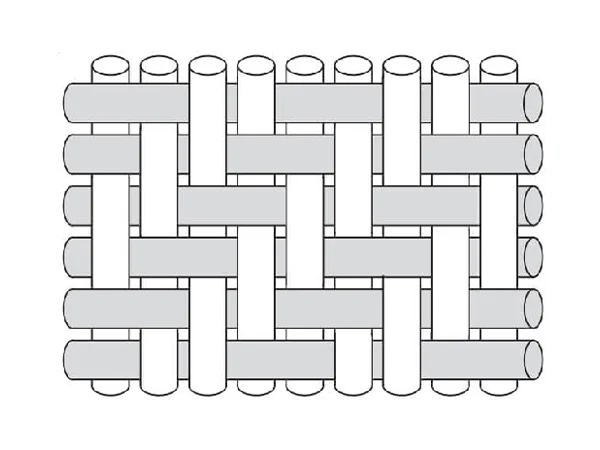
Double Twill Weave
Double twill weave is used in situations requiring high-density tight weaving. The characteristic of double twill weave is the diagonal or slanting lines.
Glass Fiber Non-Woven Fabric
Fiberglass non-woven filter fabric (non-woven fabric) is a filter material made from glass fiber through a non-woven process. The non-woven process binds fibers together through methods such as wet-laid, needle punching, and melt-blown, unlike traditional weaving processes that interlace fibers. Glass fiber non-woven filter fabric typically has advantages such as high strength, high-temperature resistance, and chemical corrosion resistance, making it suitable for filtration work in harsh environments such as high temperature, high humidity, and corrosive gases. It is widely used in industrial fields such as air filters, liquid filters, automotive filters, etc.
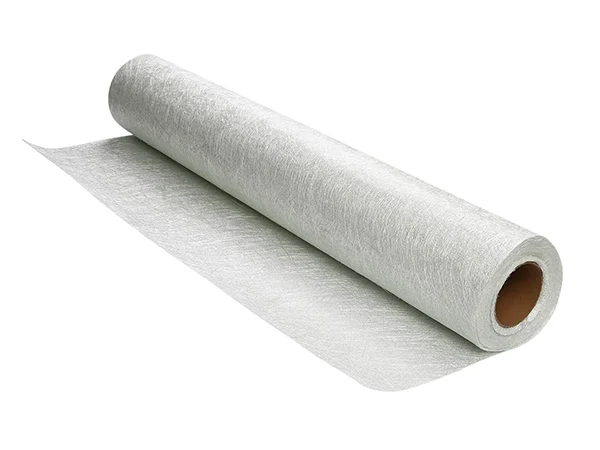

| Item | Material Type |
|---|---|
| Main Material | Alkali-free glass fiber |
| Medium-alkali glass fiber | |
| Composite Material | Polyimide (P84), Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), Metas, Polyamide-imide, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), etc. |
| Coating | Composite expanded microporous polytetrafluoroethylene film (ePTFE) |